1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
| """
1:链表介绍
概述:
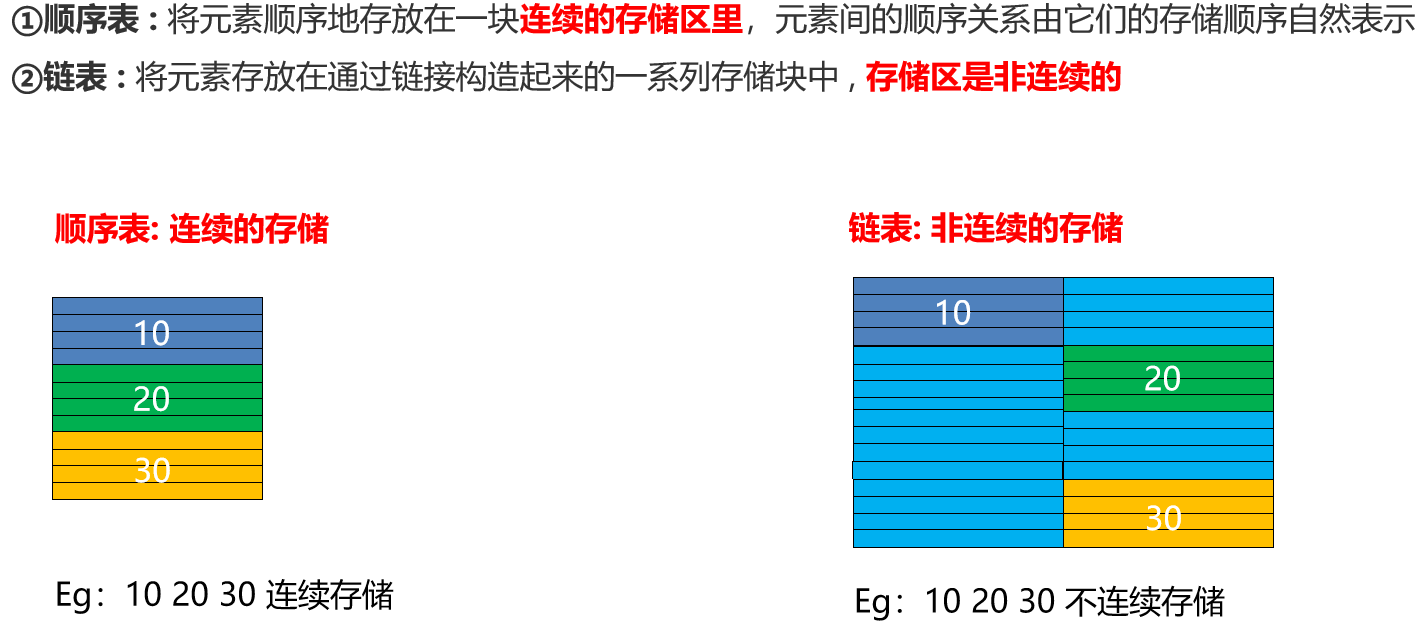
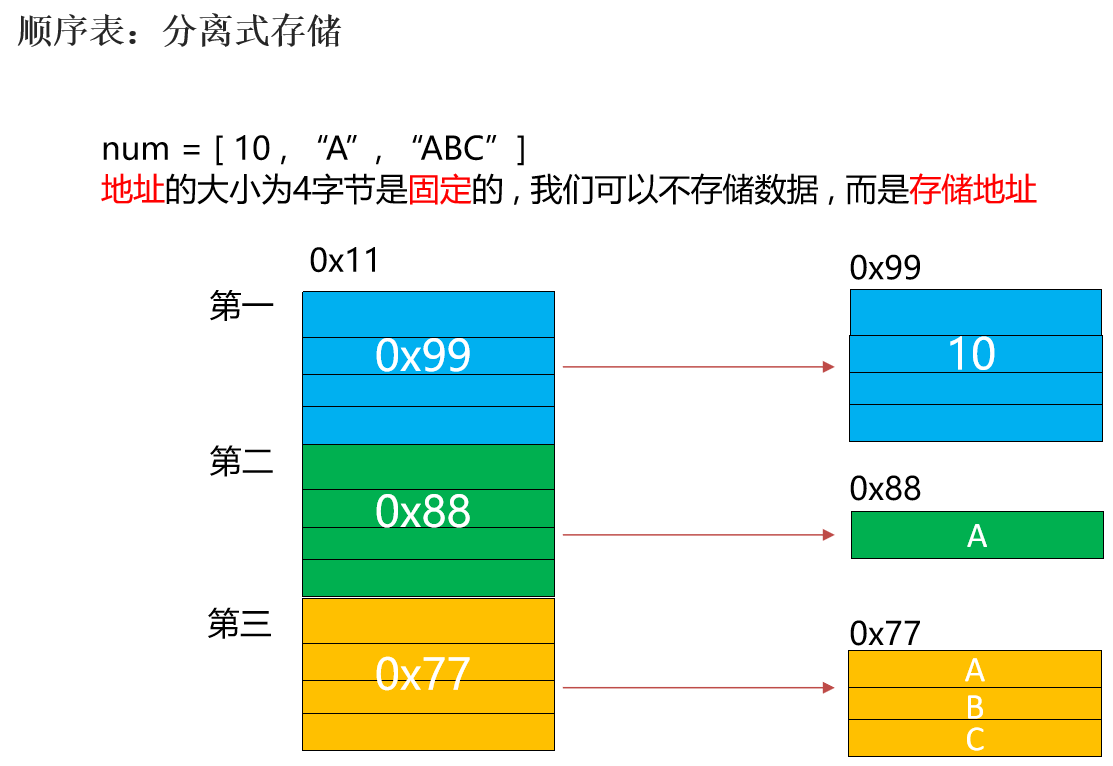
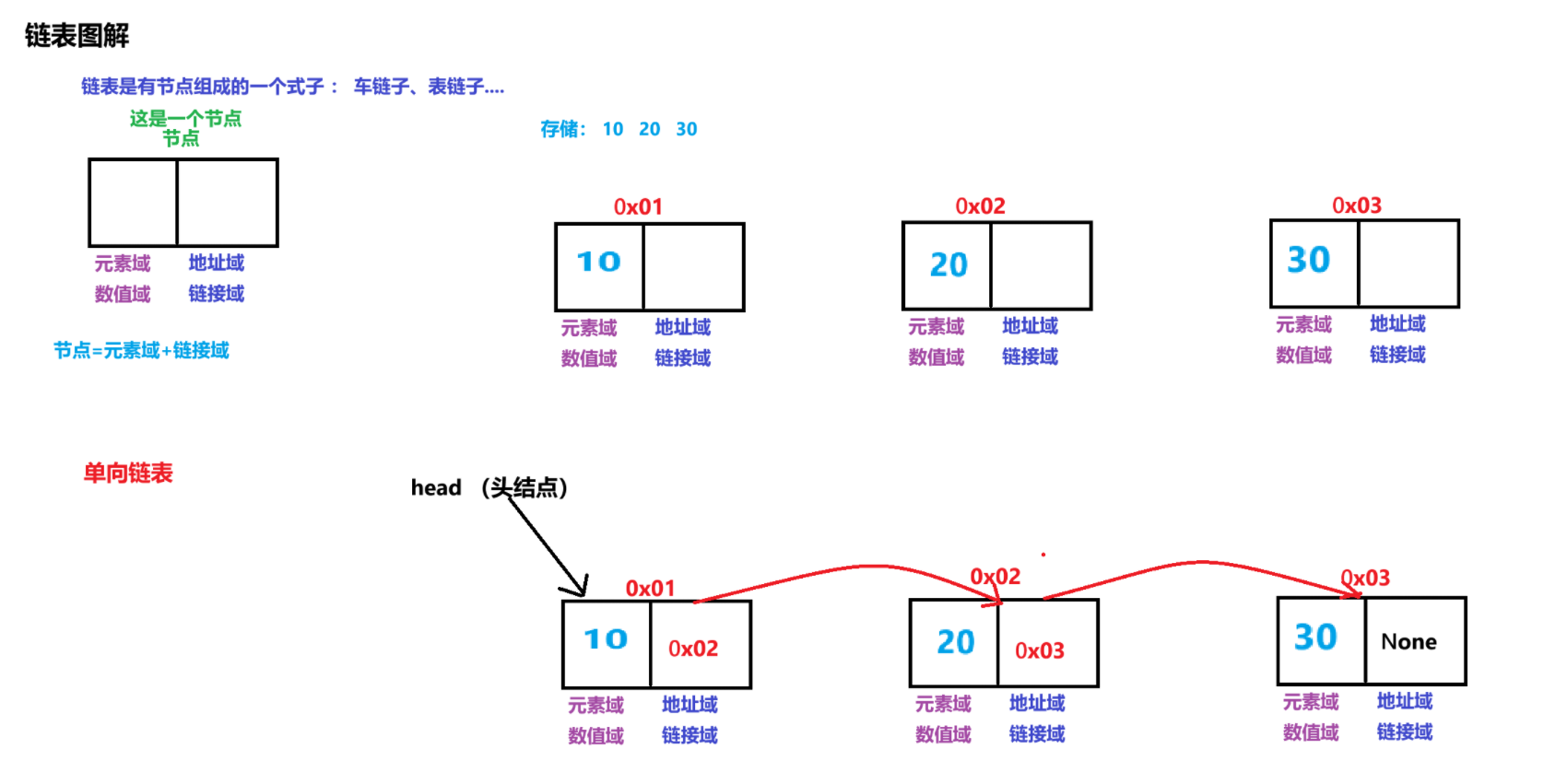
他是数据结果的线性结构的一种,每一个阶段只有一个前驱和一个后继
作用:
优化顺序表的弊端(如果没有足够的内存空间,会导致扩容失败)
链表的扩容,有地就行。连不连续无所谓
组成:
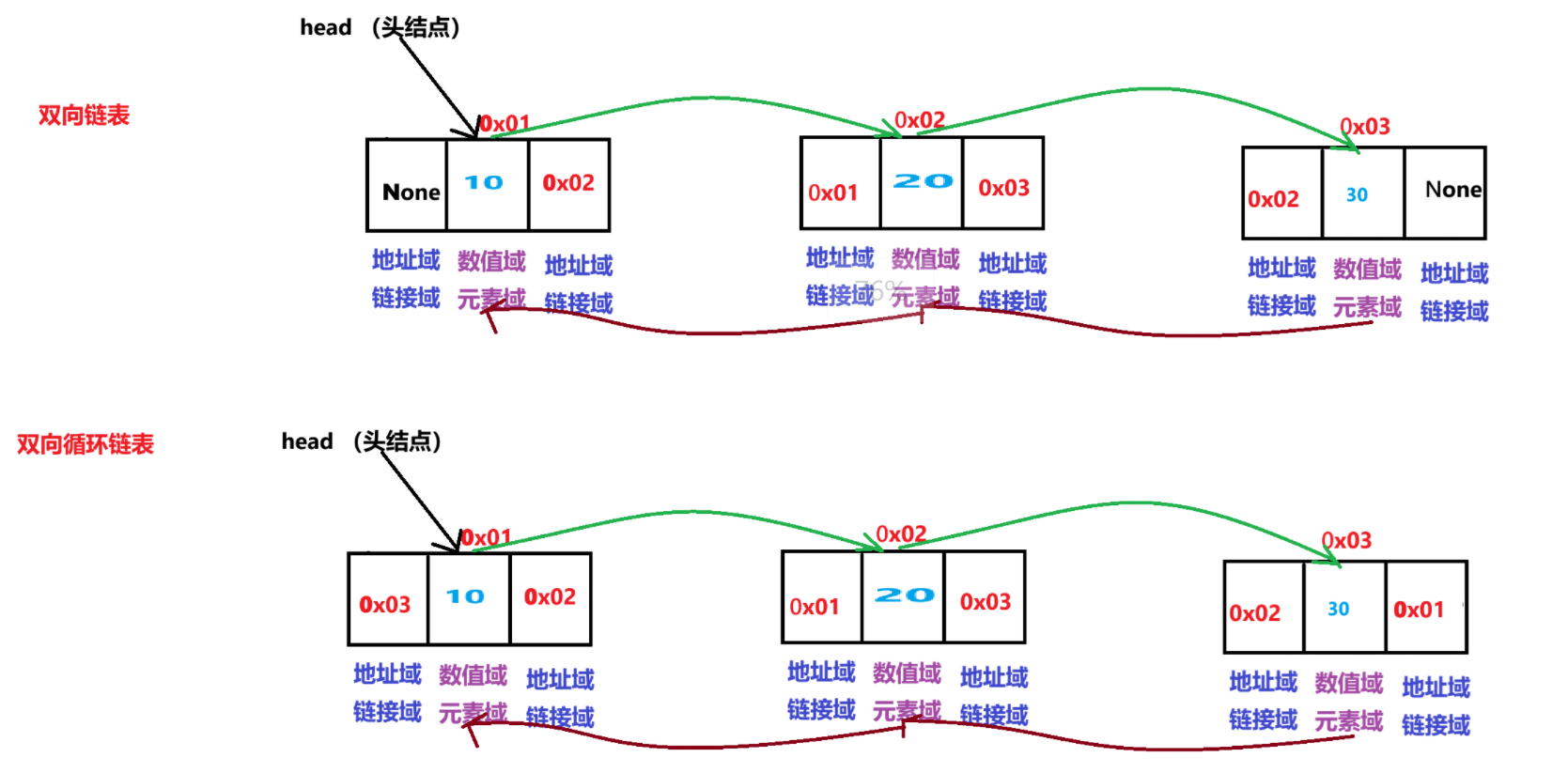
链表 有 节点 组成 ,节点由 元素域 和链接域 组成
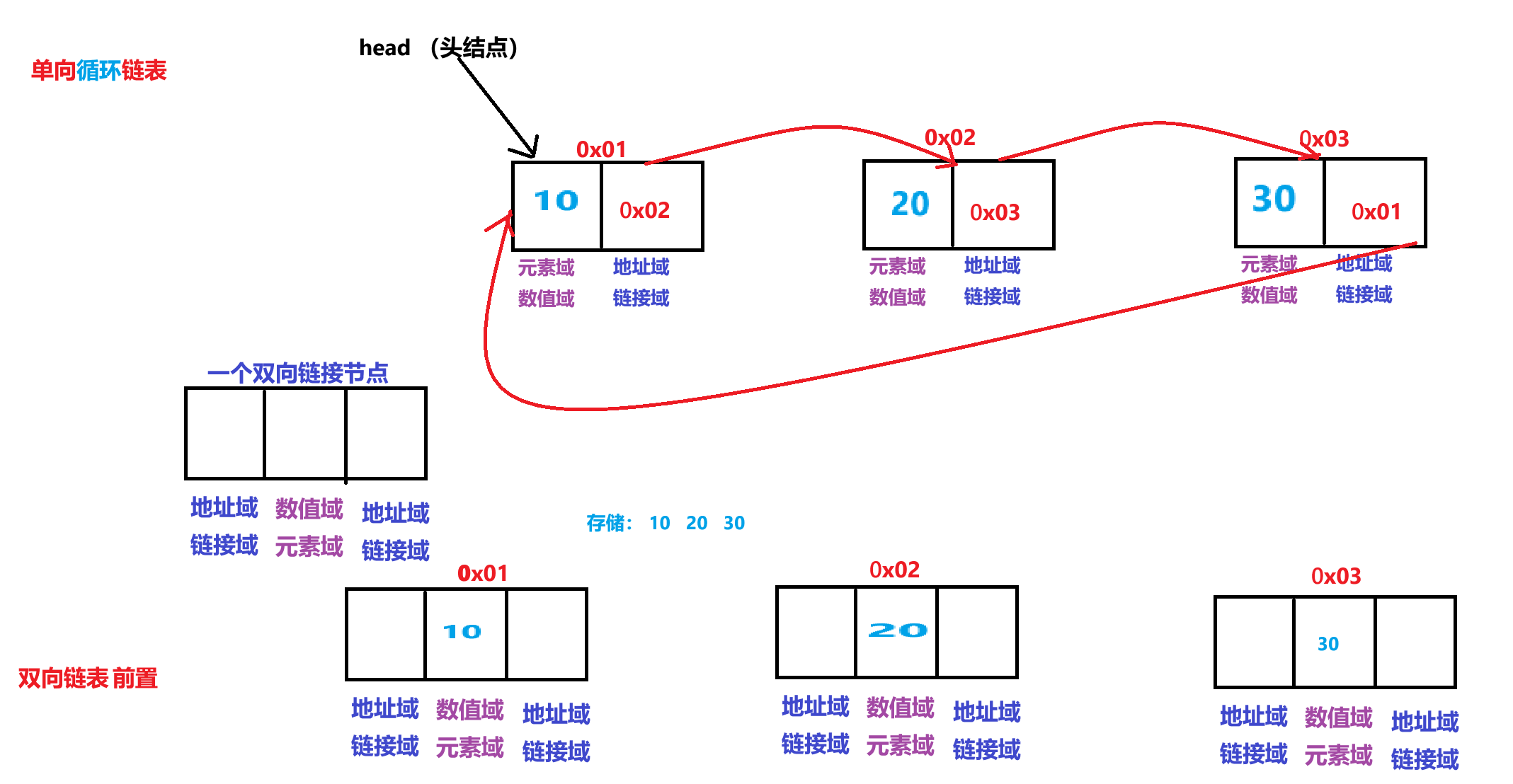
分类:
单链表
单循环链表
双链表
双循环链表
自定义代码模拟链表 思路分析:
1:自定义SingleNode类 表示节点类
属性:
item 数值域(元素域)
next 地址域(链接域) 不是他的地址,而是他的下一个节点地址
2:自定义SingleLinkedList类 表示:链表
属性:
head 表示头结点 ,指向链表的第一个节点
行为:
is_empty(self) :链表是否为空
length(self):判断链表长度
traverse(self):遍历整个链表
add(self,item) :给链表头部添加元素
append(self,item):链表尾部添加元素
insert(self,item):指定位置添加元素
remove(self,item):删除节点
search(self,item):查询节点是否存在
"""
class SingleNode:
def __init__(self, item):
self.item = item
self.next = None
class SingleLinkList:
def __init__(self, node=None):
self.head = node
def is_empty(self):
return self.head is None
def length(self):
cur = self.head
count = 0
while cur is not None:
count += 1
cur = cur.next
return count
def traverse(self):
cur = self.head
while cur is not None:
print(f"数值域:{cur.item}", end="")
cur = cur.next
def add(self, item):
new_node = SingleNode(item)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def append(self, item):
new_node = SingleNode(item)
if self.is_empty():
self.head = new_node
else:
cur = self.head
while cur.next is not None:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = new_node
def insert(self, pos, item):
if pos <= 0:
self.add(item)
elif pos >= self.length():
self.append(item)
else:
cur = self.head
count = 0
while count < pos - 1:
cur = cur.next
count += 1
new_node = SingleNode(item)
new_node.next = cur.next
cur.next = new_node
def remove(self, item):
cur = self.head
pre = None
while cur is not None:
if cur.item == item:
if cur == self.head:
self.head = cur.next
else:
pre.next = cur.next
cur.next = None
return
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
def search(self, item):
cur = self.head
while cur is not None:
if cur.item == item:
return True
cur = cur.next
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
node1 = SingleNode(10)
print(f"元素域(数值域):{node1.item}")
print(f"链接域(地址域):{node1.next}")
print(f"node1对象{node1}")
print(f"node1类型{type(node1)}")
print("---------------测试链接类-------------------")
my_linklist = SingleLinkList(node1)
print(f"头结点:{my_linklist}")
print(f"头节点的元素域{my_linklist.head.item}")
print(f"头节点的地址域{my_linklist.head.next}")
print("---------------测试链表是否为空-------------------")
print(my_linklist.is_empty())
print("---------------测试头插-------------------")
my_linklist.add(20)
my_linklist.add(30)
print("---------------测试尾插-------------------")
my_linklist.append(40)
my_linklist.append(50)
print("---------------测试任意位置插入-------------------")
my_linklist.insert(-1, 2)
my_linklist.insert(8, 55)
my_linklist.insert(2, 32)
print("---------------测试删除-------------------")
my_linklist.remove(2)
my_linklist.remove(30)
my_linklist.remove(60)
print("---------------测试查找-------------------")
print(my_linklist.search(2))
print(my_linklist.search(32))
print("---------------测试链表长度-------------------")
print(f"当前链表长度为:{my_linklist.length()}")
print("---------------测试遍历-------------------")
my_linklist.traverse()
|