01 1、什么是Function Call? 概念:大模型基于具体任务,智能决策何时需要调用某个函数,同时返回符合函数参数的 JSON对象。
能力获得的方式:基于训练来得到的,所以并不是所有大模型都具有Function Call能力。
优势:信息实时性、数据局限性、功能扩展性。
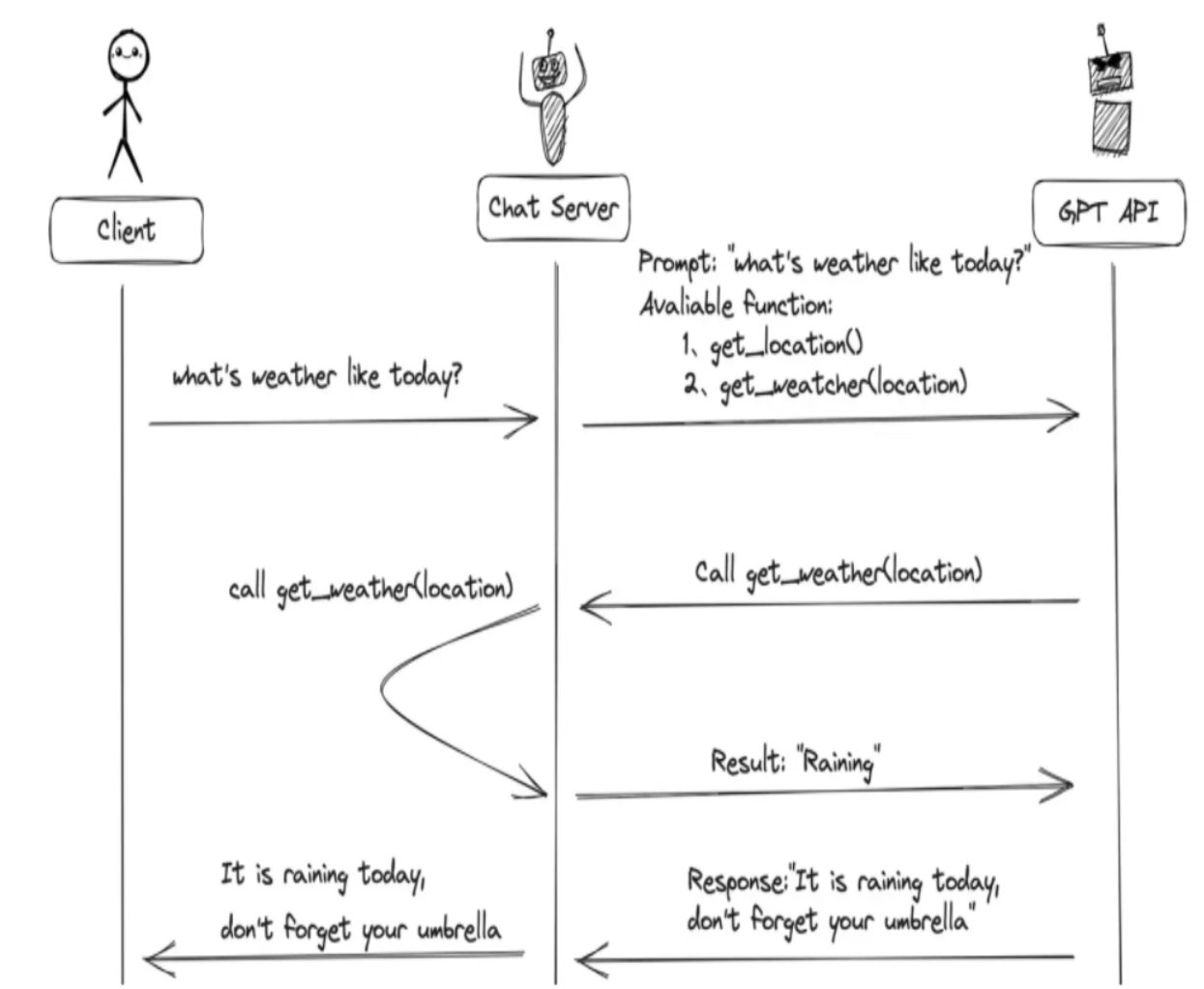
2、Function Call 工作原理是什么? 主要步骤:
用户(客户端)发送请求和提示词,聊天服务器(Chat Server)将该提示词以及当前可调用的函数列表一并发送给大模型。
大模型根据提示词的内容和上下文,判断应生成普通文本回复,还是以函数调用的格式进行响应。
如果模型决定调用函数,它会返回一个包含函数名称和参数的结构化调用指令;聊天服务器接收到该指令后,执行对应的函数,并将函数的实际执行结果返回给大模型。
模型再根据函数返回的数据,将其整合并生成一段自然、连贯的文本作为最终回复,返回给用户。
3、Function Call的使用方式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 @tool def add (a: int , b: int ) -> int : """ 将数字a与数字b相加 Args: a: 第一个数字 b: 第二个数字 """ return a + b @tool def multiply (a: int , b: int ) -> int : """ 将数字a与数字b相乘 Args: a: 第一个数字 b: 第二个数字 """ return a * b tools = [add, multiply] llm = ChatOpenAI(base_url=conf.base_url, model=conf.model_name, api_key=conf.api_key, temperature=0.2 ) llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools, tool_choice="auto" ) query = "2+1等于多少?" messages = [HumanMessage(query)] try : ai_msg = llm_with_tools.invoke(messages) messages.append(ai_msg) print (f"\n第一轮调用后结果:\n{messages} " ) if hasattr (ai_msg, "tool_calls" ) and ai_msg.tool_calls: for tool_call in ai_msg.tool_calls: func = {"add" : add, "multiply" : multiply}[tool_call["name" ].lower()] tool_result = func.invoke(tool_call["args" ]) messages.append(ToolMessage(content=tool_result, tool_call_id=tool_call["id" ])) print (f"\n工具调用结果添加到messages后:\n{messages} " ) final_response = llm_with_tools.invoke(messages) print (f"\n最终模型响应:\n{final_response.content} " ) else : print ("模型未生成工具调用,直接返回文本:" ) print (ai_msg.content) except Exception as e: print (f"调用失败:{e} " )
4、什么是MCP协议? MCP(Model Context Protocol,模型上下文协议)是由 Anthropic 在2024年1月提出的一套开放协议,旨在实现大型语言模型(LLM)与外部数据源和工具的无缝集成,用来在大模型和数据源之间建立安全双向的链接 。也就是说,将这些外部数据源和工具进行统一管理,以方便大模型进行统一调用。
5、MCP 工具调用流程
客户端连接多个 MCP Server,获取并缓存工具清单。
LLM 通过这些清单“知道”有哪些可用工具。
LLM 根据用户请求决定调用哪个工具,并发出调用指令。
MCP Client 把指令转发给对应 Server,Server 执行工具逻辑。
结果返回给 Client,再传回 LLM,生成最终回答。
6、MCP的通信传输方式有哪些? Stdio:本地进程间通信 ,部署简单、延迟低。适合私有化或本地化场景;缺点是不能跨网络使用。
SSE(Server-Sent Events):SSE 是一种 基于 HTTP 的单向推送协议 ,它允许服务器在保持连接开放的情况下,持续向客户端发送事件流。适用于简单、单向的数据推送;但需要维护长连接,对横向扩展和断连重连有额外设计成本。
Streamable HTTP:也是一种基于 HTTP 的传输方式,支持双向传输和流式传输 ,集成云/负载均衡器更方便,灵活性和工程友好度使其成为当前主流选择。
7、服务端和客户端使用示例 服务端:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCPmcp = FastMCP("sdg" , log_level="ERROR" , host="127.0.0.1" , port=8001 ) @mcp.tool( name="query_high_frequency_question" , description="从知识库中检索常见问题解答(FAQ),返回包含问题和答案的结构化JSON数据。" , async def query_high_frequency_question () -> str : return "高频问题是: 恐龙是怎么灭绝的?" if __name__ == "__main__" : mcp.run(transport="streamable-http" )
客户端:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 from mcp.client.streamable_http import streamablehttp_clientfrom langchain.agents import create_tool_calling_agent, AgentExecutorfrom langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplatefrom langchain_mcp_adapters.tools import load_mcp_toolsfrom langchain_openai import ChatOpenAIfrom mcp import ClientSessionimport asynciofrom agent_learn.config import Configconf = Config() llm = ChatOpenAI(base_url=conf.base_url, api_key=conf.api_key, model=conf.model_name, temperature=0.1 ) server_url = "http://localhost:8001/mcp" async def main (): global mcp_client async with streamablehttp_client(url=server_url) as (read, write, _): async with ClientSession(read, write) as session: await session.initialize() tools = await load_mcp_tools(session) prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([ ("system" , "你是一个乐于助人的助手,能够调用工具回答用户问题。" ), ("human" , "{input}" ), ("placeholder" , "{agent_scratchpad}" ), ]) agent = create_tool_calling_agent(llm, tools, prompt_template) agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools, verbose=True ) query = "北京天气如何?" response = await agent_executor.ainvoke({"input" : query}) print (f"response-->{response} " ) return if __name__ == '__main__' : asyncio.run(main())
02 1、用python_a2a包如何创建MCP服务器和客户端? 服务端:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import uvicornfrom python_a2a.mcp import FastMCPfrom python_a2a.mcp import create_fastapi_appmcp = FastMCP( name="MyMCPTools" , description="提供高频问题和天气查询工具" , version="1.0.0" ) @mcp.tool( name="get_weather" , description="查询天气" async def get_weather (**kwargs ) -> str : return '{"status": "success", "data": "北京的天气是多云"}' app = create_fastapi_app(mcp) uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0" , port=8010 )
客户端(agent调用):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 from mcp.client.streamable_http import streamablehttp_clientfrom langchain.agents import create_tool_calling_agent, AgentExecutorfrom langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplatefrom langchain_mcp_adapters.tools import load_mcp_toolsfrom langchain_openai import ChatOpenAIfrom mcp import ClientSessionimport asynciofrom python_a2a import MCPClient, to_langchain_toolfrom agent_learn.config import Configconf = Config() llm = ChatOpenAI(base_url=conf.base_url, api_key=conf.api_key, model=conf.model_name, temperature=0.1 ) async def main (): url = "http://localhost:8010" mcp_client = MCPClient(server_url=url) try : tools = await mcp_client.get_tools() get_weather_tool = to_langchain_tool(url, "get_weather" ) query_high_frequency_question = to_langchain_tool(url, "query_high_frequency_question" ) tools = [get_weather_tool, query_high_frequency_question] prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([ ("system" , "你是一个乐于助人的助手,能够调用工具回答用户问题。" ), ("human" , "{user_input}" ), ("placeholder" , "{agent_scratchpad}" ), ]) agent = create_tool_calling_agent(llm, tools, prompt_template) agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools, verbose=True ) query = "北京天气如何?" response = await agent_executor.ainvoke({"user_input" : query}) except Exception as e: print (f"Error: {e} " ) if __name__ == '__main__' : asyncio.run(main())
2、什么是Agent? Agent就是基于大模型的语义理解和推理能力,让大模型拥有解决复杂问题时的任务规划能力,并调用外部工具来执行各种任务,并且能够保留“记忆”的一个智能体。
Agent = 大模型 + 任务规划(Planning) + 使用外部工具执行任务(Tools&Action) + 记忆(Memory)
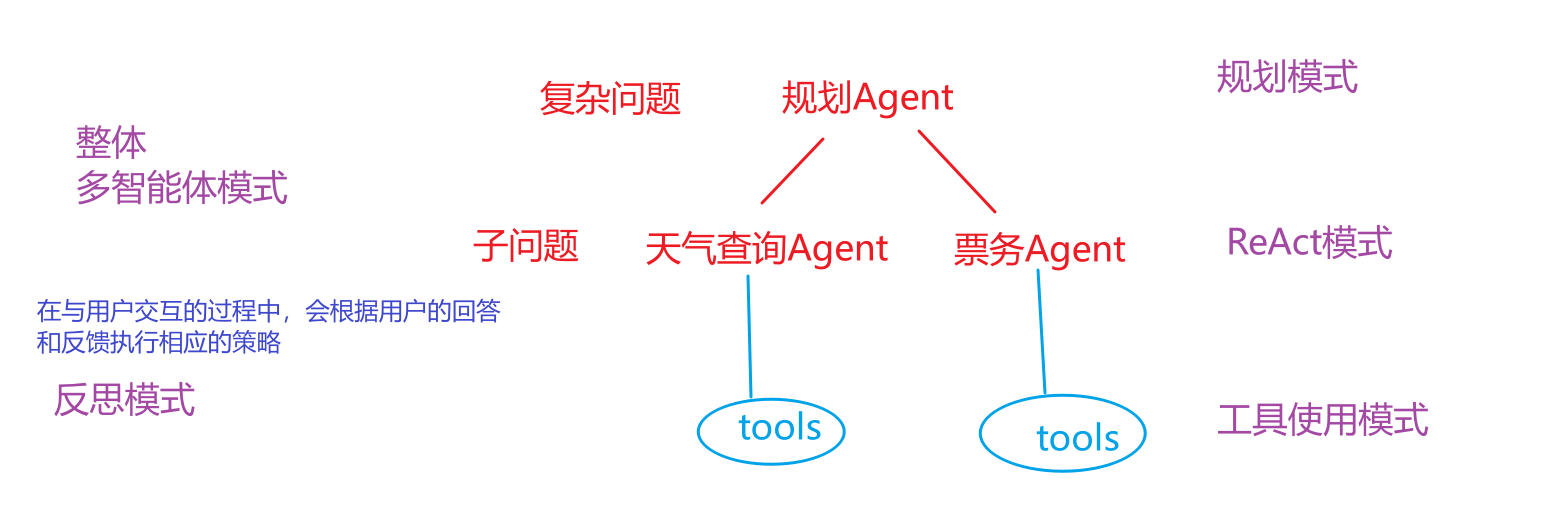
3、Agent有哪几种常见的模式? (1)⼯具使⽤模式
允许 Agent 调用外部工具来弥补自身知识的不足。
agent会自动完成工具的选择和调用,并基于工具调用结果进行最终答案生成。
(2)ReAct 模式
将“思考”(Reasoning)和 “行动”(Acting)紧密地结合在一起,形成一个动态的循环。这个模式让Agent不再是简单地调用工具,而是像人类一样“边想边做” ,从而解决更复杂的问题。
**工作流程:**思考——》行动——》行动输入——》观察——》循环迭代
(3)反思模式
Agent 在完成一个步骤或整个任务后,对其结果进行评估生成反馈【大模型自身、评估模型、调用工具、用户反馈】, 然后Agent根据反馈结果进行反思并对结果进行修正。
(4)规划模式
先将一个大目标分解成一个详细的、有序的计划(Plan),然后再逐一执行计划中的每个步骤(每个步骤可能是一个 ReAct 循环)。
(5)多智能体模式
可以设计多个具有不同角色和能力的 Agent,让它们协同工作来完成极复杂的任务。
4、项目中用到了哪些模式? 一个真正强大的 Agent 系统,并不会只使用其中一种模式。它会根据任务的复杂性,灵活地将这些模式组合起来。例如,一个 Agent 面对一个复杂问题时,可能会先启动 规划模式 来分解任务,然后将子任务交给一个使用 ReAct 模式 的执行者,而这个执行者在执行过程中又会调用各种 工具 ,并在遇到困难时启动 反思模式 来修正自己的策略。
5、什么是A2A协议? ==A2A协议就是不同智能体进行沟通协作的协议。==
作用:
安全协作(可以保证agent之间的交互信息是安全的)
任务与状态管理(提交一个任务后,可以跟踪任务的状态和处理结果)
用户体验协商(智能体可以根据用户的问题和反馈进行调整,提高用户的体验)
能力发现(agent通过AgentCard 来展示自己的功能,其他agent可以自动读取AgentCard 中的信息来了解该智能体的功能)
6、Agent2Agent 核心概念有哪些? AgentSkill :AgentSkill 定义了单个智能体(Agent)所具备的、可被外部调用的具体功能或能力。
AgentCard :AgentCard 是描述一个智能体身份、能力(AgentSkill)、接口信息和元数据的标准化声明文件,用于代理发现和服务注册。
Task :Task 指的是具体的需要完成目标,会包含关于session_id、状态、任务的内容、处理结果等信息。
TaskState :TaskState是任务状态枚举类,定义了任务的可能状态,包括SUBMITTED/COMPLETED等。
TaskStatus :TaskStatus 表示 A2A 任务的当前状态对象,包括状态枚举(TaskState)、附加消息和时间戳。
A2AServer :A2AServer是A2A协议的核心实现类,用于 构建代理服务器 。
artifacts :artifacts 是 A2A 协议中 Task 对象的核心字段之一,用于存储任务执行后的输出产物(结果)。
AgentNetwork :AgentNetwork 是 A2A 协议中的agent网络管理类,用于集中管理和发现 A2AServer。
AIAgentRouter :AIAgentRouter 是负责根据任务需求和 AgentCard 信息,将任务路由到最合适智能体的组件。
03 1、AIAgentRouter 是干嘛的?如何使用? AIAgentRouter 是使用 LLM 智能路由查询到合适agent的类,它用来分析查询意图和上下文,选择最佳代理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 from python_a2a import AIAgentRouter, AgentNetworkfrom langchain_openai import ChatOpenAIfrom agent_learn.config import Configconf=Config() network = AgentNetwork(name="MyNetwork" ) network.add("TicketAgent" , "http://127.0.0.1:5010" ) llm = ChatOpenAI(base_url=conf.base_url, api_key=conf.api_key, model=conf.model_name, temperature=0.1 ) router = AIAgentRouter(llm_client=llm, agent_network=network) question = "定一张北京去上海的火车票" agent_name, confidence = router.route_query(question) print (f"{agent_name} {confidence} " )client = network.get_agent(name=agent_name) print (client.ask(question))
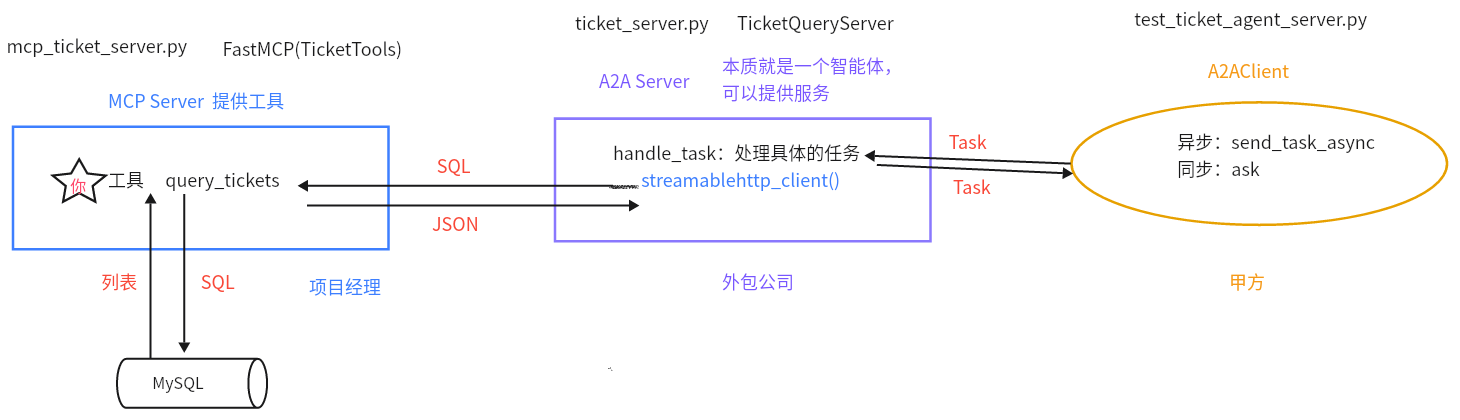
2、A2AServer如何与MCP Server结合使用? 首先创建MCP Server,然后创建A2AServer子类,在子类的init方法中创建MCPClient对象,在子类handle_task中,通过MCPClient对象调用具体的工具,然后将处理结果放到artifacts中进行返回。创建好A2AServer子类后,可以用A2AClient进行调用。
核心代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class WeatherServer (A2AServer ): def __init__ (self ): super ().__init__(agent_card=agent_card) self .mcp_client = MCPClient('http://127.0.0.1:6005' ) def handle_task (self, task ): print ("收到A2A任务的task:=>" , task) query = (task.message or {}).get('content' , {}).get('text' , '' ) if "天气" in query: city = "北京" weather_result = asyncio.run(self .mcp_client.call_tool(tool_name="get_weather" , city=city)) print ("天气查询结果:=>" , weather_result) task.artifacts = [{"parts" : [{"type" : "text" , "text" : weather_result}]}] else : task.artifacts = [{"parts" : [{"type" : "text" , "text" : "无法理解的任务" }]}] task.status = TaskStatus(TaskState.COMPLETED) return task
3、如何异步调用AgentServer? 1 2 3 4 5 6 message_weather = Message(content=TextContent(text=weather_query), role=MessageRole.USER) task_weather = Task(id ="task-" + str (uuid.uuid4()), message=message_weather.to_dict()) weather_result_task = await weather_client.send_task_async(task_weather)
4、复杂任务如何拆解? 使用任务拆解agent (大模型,用提示词的方式),将复杂任务拆解成子任务。【同agent的规划模式】
核心代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 conf = Config() decompose_llm = ChatOpenAI( model=conf.model_name, api_key=conf.api_key, base_url=conf.base_url, temperature=0.1 , streaming=True ) decompose_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(""" 将以下用户查询分解为独立的子查询,每个子查询对应一个单一意图。 返回 JSON 格式的列表:{{"sub_queries": ["子查询1", "子查询2", ...]}} 示例: 查询: "预订票,查天气" 输出: {{"sub_queries": ["预订票", "查天气"]}} 查询: {query} """ )decompose_chain = decompose_prompt | decompose_llm | StrOutputParser() try : decompose_result = decompose_chain.invoke({"query" : query}) decompose_response = re.sub(r'^```json\n|\n```$' , '' , decompose_result.strip()) decompose_data = json.loads(decompose_response) sub_queries = decompose_data.get("sub_queries" , [query]) except Exception as e: print (f"[主控日志] 分解失败: {e} " ) sub_queries = [query]
5、如何做到任务的并行? 先将任务的协程对象进行保存,然后调用asyncio.gather()一起执行这些任务。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 message = Message(content=TextContent(text=sub_query), role=MessageRole.USER) agent_task = Task(message=message.to_dict(), id ="task-" + str (uuid.uuid4())) tasks.append(agent_client.send_task_async(agent_task)) results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True )
6、项目中是如何获取天气信息的? 每隔1小时 从和风天气中拉取最新的数据更新到MySQL数据库中,然后在查询天气时,直接从MySQL中获取最新的数据。
这样做的原因是减少直接访问API带来的成本消耗,并且可以降低网络请求的延迟,提高用户的体验。
表结构如下:
注意:虽然在我们这个项目中,票务信息也是存储在MySQL中,从MySQL中获取的余票信息,但是实际工作中票的信息变化比较快,所以一般是通过调用API的方式来获取实时的余票信息。
04 1、简单描述一下数据爬取的流程? 我们的天气数据是从和风网上爬取过来的,主要是调用API获取数据,然后存储在MySQL中。我们是每隔1小时检查一下,每个城市数据的最新更新时间,如果最新更新时间距离现在大于了1小时,则进行更新。更新时先去拉取对应城市的数据,然后==upsert==到数据库中。
2、详细介绍一下天气MCP服务器是怎么做的? 使用的是mcp模块,先去创建FastMCP的对象,然后构建工具函数,并使用tool进行注解,最后启动这个服务器。其中工具函数就是输入一个sql查询语句,然后查询数据库获取天气数据,最后对结果进行解析 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCPdef create_weather_mcp_server (): weather_mcp = FastMCP(name="WeatherTools" , instructions="天气查询工具,基于 weather_data 表。" , log_level="ERROR" , host="127.0.0.1" , port=8002 ) service = WeatherService() @weather_mcp.tool( name="query_weather" , description="查询天气数据,输入 SQL,如 'SELECT * FROM weather_data WHERE city = \"北京\" AND fx_date = \"2025-07-30\"'" ) def query_weather (sql: str ) -> str : logger.info(f"执行天气查询: {sql} " ) return service.execute_query(sql) weather_mcp.run(transport="streamable-http" ) if __name__ == '__main__' : create_weather_mcp_server()
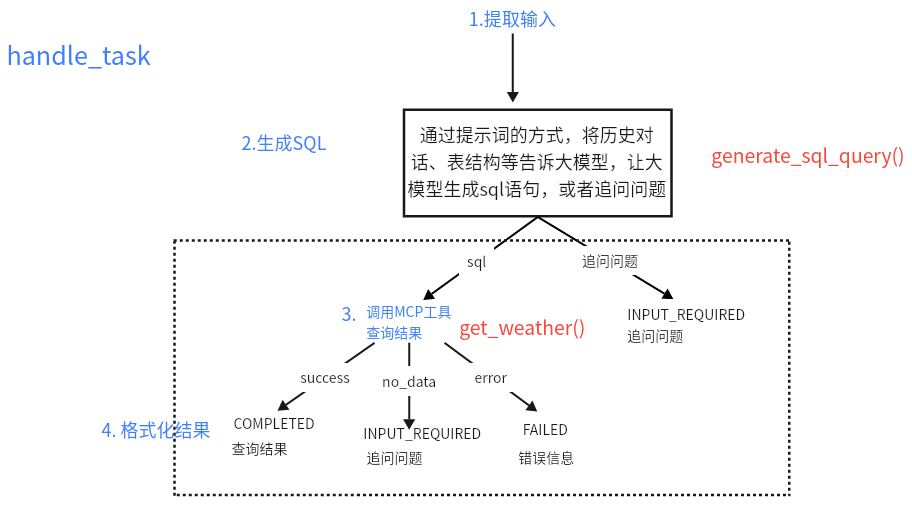
3、天气agent服务器是如何做的? NLP2SQL:首先通过提示词的方式,将历史对话、表结构等告诉大模型,让大模型生成sql语句,或者追问问题。
定义agent server,在handle_task中实现MCP工具的调用:然后自定义WeatherQueryServer,继承A2AServer,实现init方法【设置agent_card】和handle_task方法【将用户的问题转成SQL,并调用MCP服务器,查询MySQL获取最终结果】。
05 1、A2AClient如何调用A2AServer,进而调用MCP中的工具?
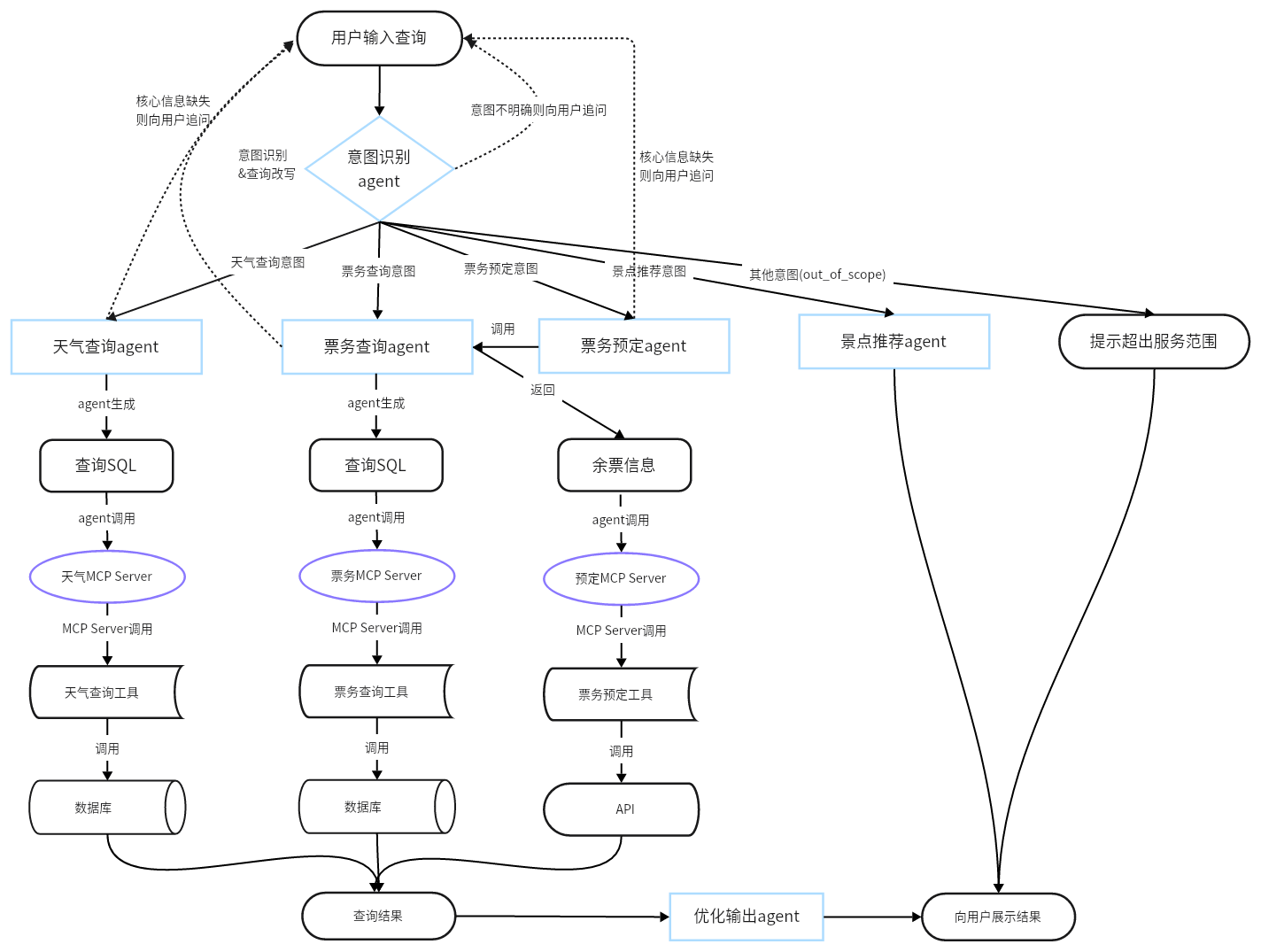
2、项目架构是怎样的?
3、为什么做意图识别和查询改写,如何做的? 原因:因为要根据用户的意图匹配不同的智能体完成具体需求的处理,所以需要进行意图识别。又因为用户的问题中经常缺乏必要的上下文信息,如果直接对该问题进行处理,效果会很差,所以需要根据用户的问题和上下文进行问题改写,生成语义完整的新问题。
做法:使用提示词的方式,将用户的问题和历史对话信息一起送到 qwen-plus 大模型中。让大模型基于这些信息识别用户的意图,并基于用户的问题和历史对话信息改写成语义完整的新问题。
4、在对话系统中历史上下文是如何来存储的? 将用户的历史对话,使用列表的方式,==循环保存==5轮在内存中,方便数据的快速取用。
另外,为实现历史对话信息查询,以及长对话场景,将对话数据==异步==存储到MySQL中进行持久化。
5、在将上下文送到大模型时,怎么做的?如果上下文过长怎么办? 动态上下文长度 :对于简单任务,如天气查询,票务查询,直接使用最近3轮对话,追加到大模型的上下文中;对于复杂任务,比如路线规划和景点推荐,需要使用长上下文时,使用GLM-4-32B模型对对话进行递归压缩 ,然后再输入大模型。
递归压缩的做法是:
分块处理:将超长上下文划分为多个片段,每块64K(GLM-4-32B支持最大输入为128K)
递归压缩:将问题和第一个分块送到大模型中进行压缩,只保留对问题有意义的内容。然后将问题、压缩结果和第二个分块送入大模型进行继续压缩。然后逐次循环直到压缩完全部分块。